What started as a free online alternative to Microsoft Office has quickly become one of the most impressive services for creating, editing, saving, syncing, and collaborating on documents. Google Drive (freemium) has long impressed me in just how far it goes toward helping groups of people work together on files simultaneously. Some new features rolling out in a recent update add even more support for teamwork.
It hasn't been long since Google Docs rebranded itself as Google Drive, so allow me to briefly recap: Google Docs took on the new name after it added local file syncing to its service. In other words, Google Docs?ahem, Drive?now works more like Dropbox , SugarSync, or any other file-syncing service you care to name, while still retaining the core office productivity apps. In that sense, its closest competitor may well be Microsoft SkyDrive, which also has online document creation tools.
With Google Drive, you can upload files to your Google account, convert them to Google's file format to edit them online, create new docs in the Web interface, collaborate with other users in real time, and export the finished products to more standard file formats, such as .doc, .rtf, .pdf, and so on. The latest round of changes makes working with others in real time even more intuitive, because you can see their profile pictures on the screen, where formerly you only saw a line of text at the top and a color code indicating who else was looking at or editing the file.
Because of these wide-ranging capabilities and its dedication to collaborative document editing, Google Drive remains a PCMag Editors' Choice. We have no hesitation recommending Google Drive?although it is important to understand how one of the new features works. The feature in question could potentially reveal your identity to others, but managing it is simple when you know how it works. And as much as Google Drive is an excellent platform and service, that doesn't mean it's the only file-syncing service you should use either.
What's New in Drive?
The newest change in Google Drive, which will roll out to users slowly, is that Google+ profile pictures of collaborators now appear at the top of the file when they're viewing or editing a document. Formerly, when collaborators opened a document, you would see a line of text reading "2 other viewers" at the top right, which opened to reveal their names or email addresses and a color code for each person. For example, if I invited Maria to edit a spreadsheet with me, I would see her name appear next to a pink square at the top of the spreadsheet any time she opened it. As she moved through cells, they would appear highlighted in pink.
The new feature adds Maria's profile picture at the top of the document and would let me add her to my Google+ circles. There's also now an integrated group chat feature that lets multiple collaborators hold discussions via text while they're working.
Another fairly big addition is offline access to all your Drive materials if you're using Google Chrome OS. To enable this setting, go to your Google Drive page and look under the "More" button the left for the offline access setting. Turning on this feature lets you read and edit your files offline; changes will sync to the cloud the next time you connect.
Privacy
The toughest criticism Google Drive has faced amount to concerns over privacy and IP ownership. The new collaboration features could put your face in front of strangers if you're not careful, but it's very easy to manage this potential problem with an ounce of care.
Some Google Drive owners keep their documents open to the public, and if you're signed into your Google account when you view these files, other users will be able to see your picture and name. When looking at public files, it's a better idea to log out of Google, or use a different browser, and maybe also turn on incognito features if your browser has them to keep yourself anonymous. Anonymous users are assigned random profile pictures of animals instead, such as a dolphin, dinosaur, or beaver.
My feeling on the matter of privacy in Google Drive is this: If you are comfortable using Gmail, you should be comfortable with Drive. If you are skeptical of Google's user agreements, don't use Google products. For more in-depth analysis, see "Google Drive's Terms of Use: Lazy People Should Worry."
Main Features of Drive
The gist of Google Drive, and the main attraction to it, is it can store your files in the cloud where they are accessible to you and your collaborators, and become highly searchable.
One feature related to "search" stands out: Google's ability to scan a photo and "read" it using optical character recognition, or identify it using its own technology. The only other app of this kind that uses built-in OCR nearly as well is Evernote , although you have to have a paid Premium account to use it.
Google also claims Drive allows videos to be uploaded, but we encountered some issues with that part of the service.
Like many other general file-syncing services, Google Drive works better for document files than multimedia. It's not ideally meant to be a music and video streaming service?for that kind of product, you'll likely need a paid service and device, such as the Verbatim Mediashare Mini, although SugarSync does offer some neat capabilities and support for streaming iTunes music. Amazon Cloud also offers some special support for music and movies. However, within the Google universe you can use Google Play in tandem with Drive (more on that in a bit).
Carryover Features from Google Docs
The core services and functionality that were in Google Docs, namely, a free online office suite where files are also hosted, remain intact in Drive. Google Docs is one of the best known free alternative to Microsoft Office, although it's entirely Web-based?there's no software to install to use it (the only downloadable part is the app for local syncing with Drive).
As with Microsoft Office, Google Drive lets you create word processing documents, spreadsheets, presentation documents, forms, vector drawings, and now in beta, tables. Google hosts your files, too, so when you log in, all your files are there. You can sort them into customizable folders, which appear along a left pane, or just search for what you need, using a standard search bar in the Web app.
When you create a document in Google Drive, the file format used is Google's own. However, the system couldn't be more flexible. You can export Google documents to more standardized files formats, like .doc, .rtf, .ppt, .pdf, and more; and you can import practically any document with the option of keeping it in its native format (which may limit your ability to edit it) or translating it into a Google doc file, which makes it editable in the online service. I've certainly had my share of moments when I was stuck on a computer that didn't have Microsoft Office at the very moment someone emailed me an important file that required my feedback pronto. Google Drive saved the day. I could open the file in GoogleDrive, edit it, and export the revised file back out to its original form. Occasionally some formatting will go haywire during this process, but it gets the job done.
Source: http://feedproxy.google.com/~r/ziffdavis/pcmag/~3/hpQ0vAJfEIY/0,2817,2403546,00.asp
nike new nfl uniforms nfl uniforms andrew bailey the village dallas fort worth tornado dallas tornadoes dallas weather





 Governments, even democracies, are not always fans of transparency. According to Google’s brand new transparency report, “government attempts to censor content on Google services has grown”, doubling since the second half of 2012 (1,054 requests vs. 2,285). Brazil took the gold medal of the censorship olympics, with 697 requests, while the United States took 2nd place, with 321 requests. Google cites an aggressive anti-negative campaigning law for half of Brazil’s spike in censorship requests. Unlike America, Brazil attempts to clamp down on any campaigns that offend the “dignity” of candidates during an election. In the most extreme example, a Brazilian judge ordered the arrest of the head of Google’s Brazil operations and the complete shutdown of all of Google’s products unless it complied with an order to remove a YouTube video attacking a mayoral candidate. In typical corporate diplomacy speak, Google writes that it is ” appealing many of these cases, on the basis that the content is protected by freedom of expression under the Brazilian Constitution.” The United States, too, has its fair share of censorship requests. While Google can’t be specific about legal matters, it appears that at least some of the requests come from overly-reactive local authorities. “We received a request from a local government agency to remove a YouTube video that allegedly defamed a school administrator,” a Google spokesman explained to us. In total, Google has complied with only 45% of requests, because they were either incomplete or violated Google’s Terms of Service (read: bald-faced attempts at censorship). In cases of clear abuse, defamation, or an overpowering government agency, Google does whip out its digital eraser. Perhaps the most concerning trend comes from the increasingly authoritarian Russia, which recently began enforcing a broad new censorship law aimed blocking objectionable content, such as child porn and information promoting suicide. Nearly all Russia’s requests (107 of 114), cite this new law. The New York Times reports that, thus far, this law has been limited to truly objectionable content, but government watchdogs fear it may be exploited for political censorship. You can read more about the transparency report here.
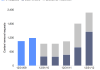
Governments, even democracies, are not always fans of transparency. According to Google’s brand new transparency report, “government attempts to censor content on Google services has grown”, doubling since the second half of 2012 (1,054 requests vs. 2,285). Brazil took the gold medal of the censorship olympics, with 697 requests, while the United States took 2nd place, with 321 requests. Google cites an aggressive anti-negative campaigning law for half of Brazil’s spike in censorship requests. Unlike America, Brazil attempts to clamp down on any campaigns that offend the “dignity” of candidates during an election. In the most extreme example, a Brazilian judge ordered the arrest of the head of Google’s Brazil operations and the complete shutdown of all of Google’s products unless it complied with an order to remove a YouTube video attacking a mayoral candidate. In typical corporate diplomacy speak, Google writes that it is ” appealing many of these cases, on the basis that the content is protected by freedom of expression under the Brazilian Constitution.” The United States, too, has its fair share of censorship requests. While Google can’t be specific about legal matters, it appears that at least some of the requests come from overly-reactive local authorities. “We received a request from a local government agency to remove a YouTube video that allegedly defamed a school administrator,” a Google spokesman explained to us. In total, Google has complied with only 45% of requests, because they were either incomplete or violated Google’s Terms of Service (read: bald-faced attempts at censorship). In cases of clear abuse, defamation, or an overpowering government agency, Google does whip out its digital eraser. Perhaps the most concerning trend comes from the increasingly authoritarian Russia, which recently began enforcing a broad new censorship law aimed blocking objectionable content, such as child porn and information promoting suicide. Nearly all Russia’s requests (107 of 114), cite this new law. The New York Times reports that, thus far, this law has been limited to truly objectionable content, but government watchdogs fear it may be exploited for political censorship. You can read more about the transparency report here. Don't write off Microsoft's chances in mobile just yet. It may still be struggling to make itself count in the smartphone space but early signs are more promising for Windows plus tablets. Microsoft has gone from having no share of the global tablet OS market in Q1 last year to taking 7.4% one year later, with 3M Windows 8 tablets shipped in Q1 2013, according to Strategy Analytics.
Don't write off Microsoft's chances in mobile just yet. It may still be struggling to make itself count in the smartphone space but early signs are more promising for Windows plus tablets. Microsoft has gone from having no share of the global tablet OS market in Q1 last year to taking 7.4% one year later, with 3M Windows 8 tablets shipped in Q1 2013, according to Strategy Analytics.




